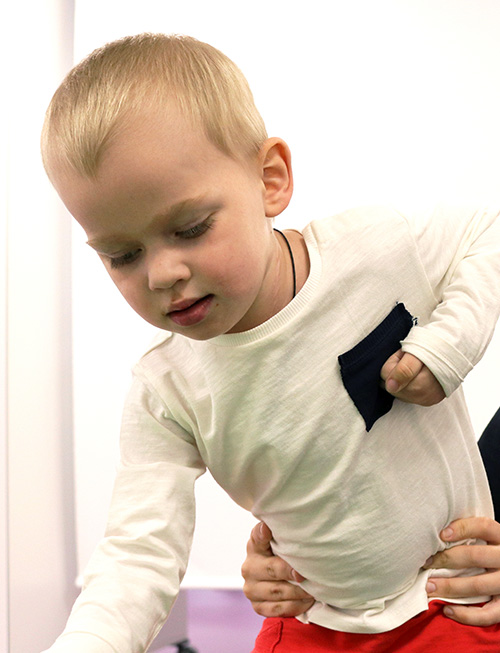
Meet the Neurorehabilitation Team
Paediatric stroke
Risk factors for paediatric stroke
We have to remember that the risk factors for paediatric stroke are totally different in this population (perinatal or postnatal) and that in many cases it is impossible to discover the trigger for the damage. We can distinguish two main groups in paediatric strokes:
- Neonatal or perinatal arterial stroke. When the stroke occurs between the 20th week of gestation and the 28th day of postnatal life.
- Postnatal arterial stroke. If the stroke occurs after 28 days of life.
The incidence of stroke or cerebrovascular accident in children under 15 years of age is approximately 6 cases per 100,000 children each year. Heart disease is one of the most frequent risk factors for a stroke in children and is considered responsible for 30% of cases. Cerebrovascular accidents are slightly more common in children under two years of age.
The main causes are:
- Birth defects.
- Infections (eg, meningitis, encephalitis).
- Trauma, operations.
- Blood disorders such as sickle cell anaemia.
Symptoms of paediatric stroke
Knowing the symptoms of paediatric stroke allows us to act quickly since people’s lack of knowledge about the possibility of a childhood stroke occurring often delays intervention and can lead to further sequelae.
We can observe the following symptoms in children:
- Facial spasms and/or dystonia.
- Apnea associated with catatonic episodes.
- Lack of mobility.
- Sudden-onset headache of a high intensity.
- Vomiting and/or nausea.
- Sudden impaired sensation in the face, arm or leg on one side of the body.
- Sudden muscle weakness on one side of the body.
- Difficulty speaking or understanding what is being said.
- Vision disorders.
- Loss of balance.
Sequelae of paediatric stroke
The prognosis of stroke in childhood, in particular ischaemic, is thought to have a better prognosis than that of adults, given the greater plasticity of the infant brain. Although strokes in children can be devastating, children have a greater healing capacity due to the greater plasticity or flexibility of the child’s nervous system and brain.
A child’s brain is still developing, so it has a greater capacity to repair itself. Many children who have suffered a paediatric stroke regain the use of their arms, legs, and speech with the help of physiotherapy and speech therapy.
The main consequences described are difficulties with language, attention, memory, visual skills and executive functioning. As well as these cognitive deficits, emotional and behavioural difficulties also appear, all of which clearly affect the child’s quality of life.
Paediatric neurorehabilitation
Paediatric neurorehabilitation plays a key role when treating a paediatric stroke. Specialised medical, surgical and rehabilitative treatment will help to restore lost functionality, minimising deficits that are secondary to the injury, and helping to gain maximum functional autonomy, quality of life, and psychomotor and educational development corresponding to the patient’s age.
The Child and Youth Rehabilitation Unit of the Institut Guttmann cares for boys and girls between the ages of 0 and 16 with physical, cognitive and behavioural functional sequelae derived from neurological diseases or injuries. We also offer regular clinical follow-up during childhood and adolescence, both to control the evolution of the disability and to prevent possible complications derived from neurological injury.
Later phases of paediatric stroke
Patients can follow personalised treatment programmes to optimise their functional capacity or address a specific problem resulting from their neurological impairment. At Guttmann Barcelona patients can find a totally personalised training and functionality improvement programme.
Guttmann Barcelona
The Guttmann Barcelona, Brain Health and Neurorehabilitation Institute offers personalised training and functional improvement programmes, as well as specialised intensive programmes.
A space that is adapted and designed for you
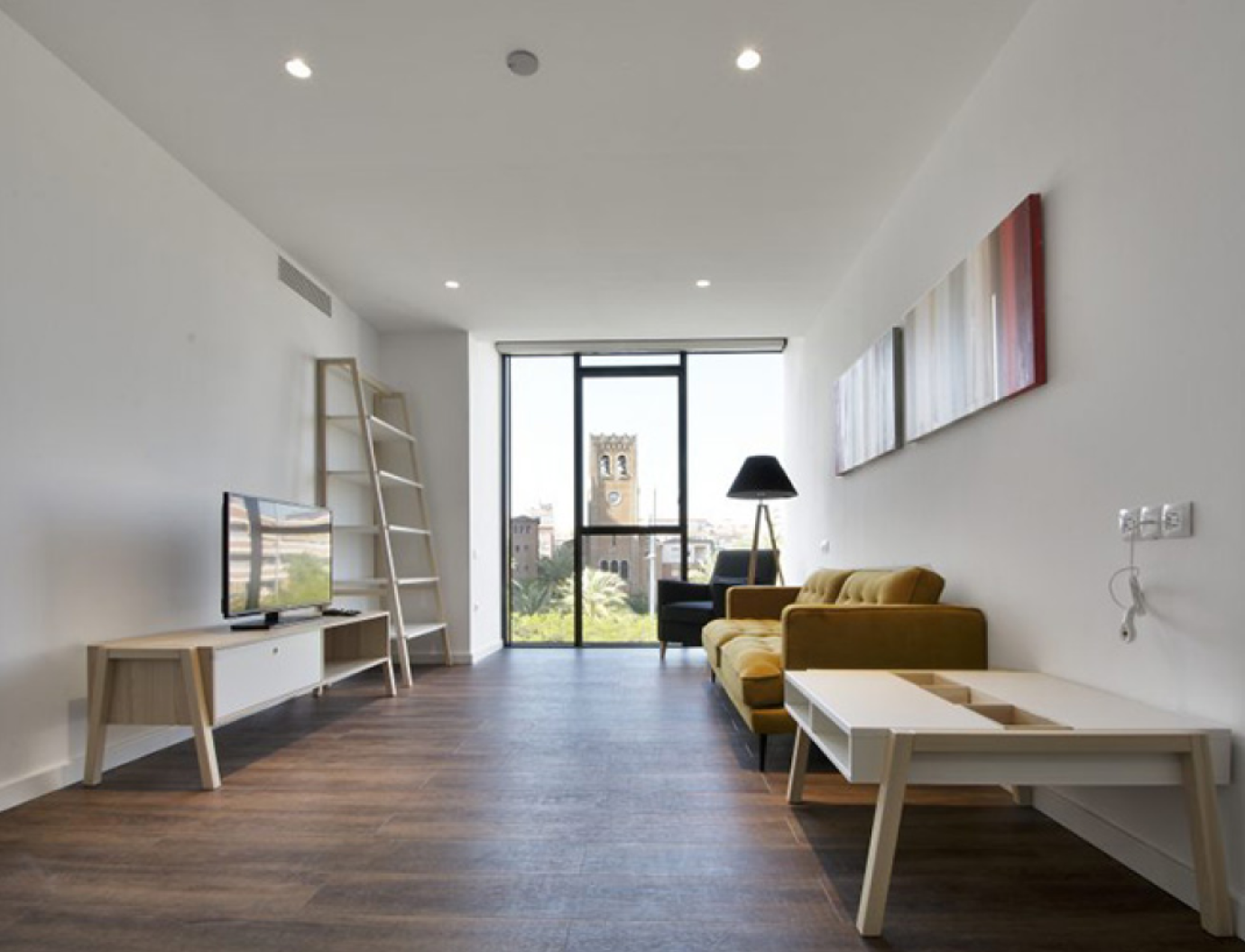
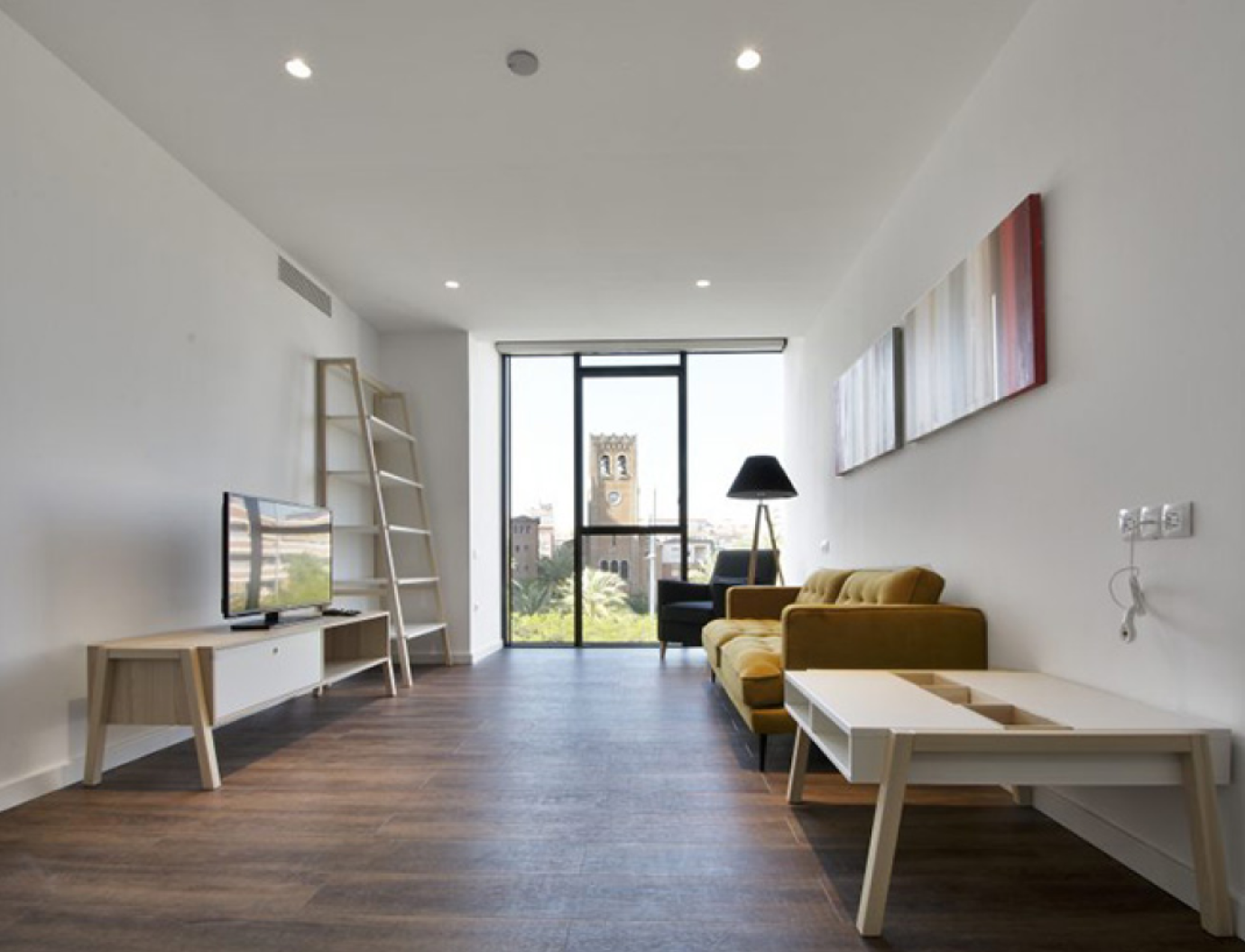
GBL apartments
Guttmann Barcelona Life is a social facility consisting of a group of fully adapted and automated apartments that offer a wide range of complementary services tailored to each user.
The apartments share a building with the Guttmann Barcelona Brain Health and Neurorehabilitation Institute, so it is possible to combine a stay with a specialised neurorehabilitation treatment.
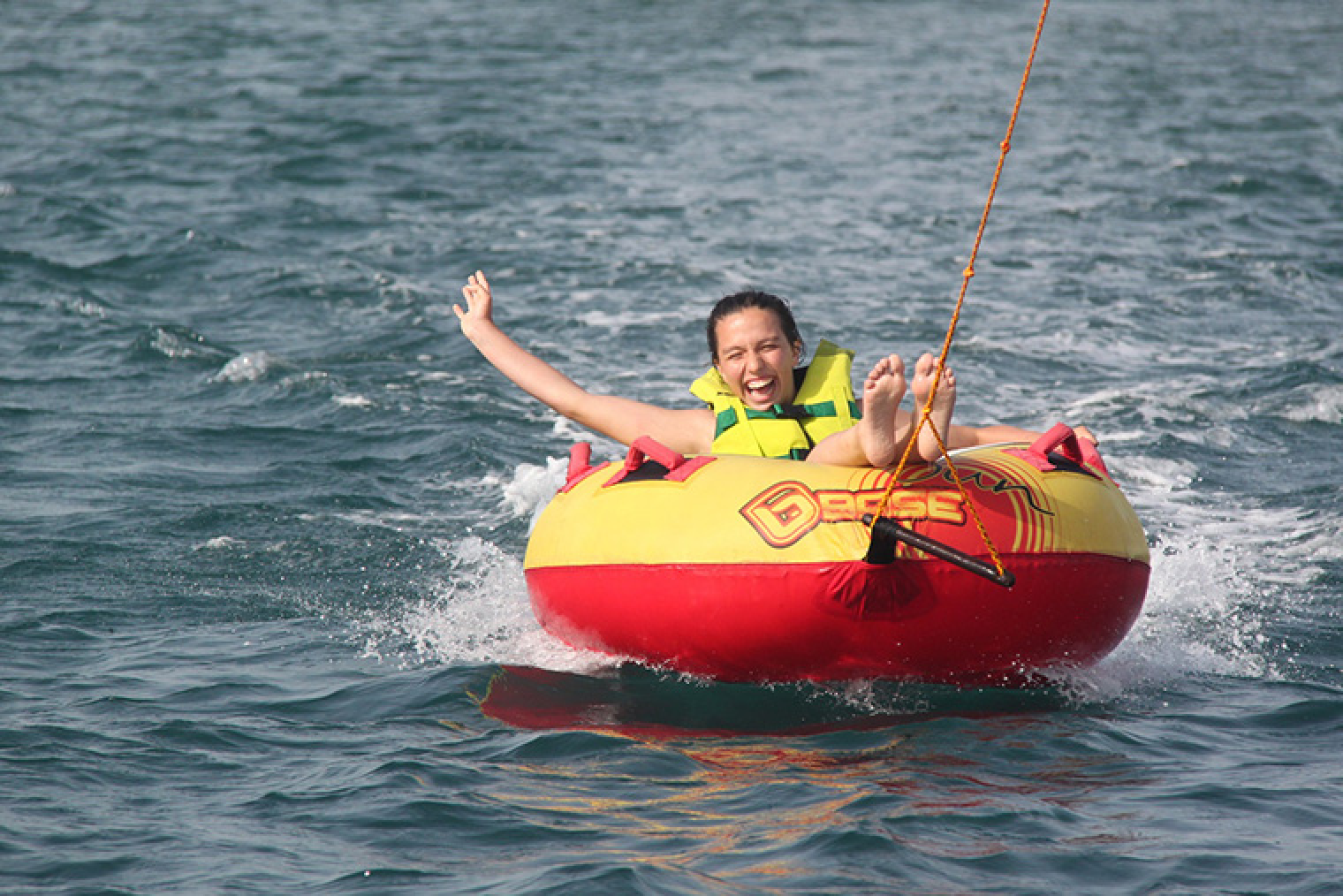
Sports camps
The Institut Guttmann regularly organises sports camps for young people between the ages of 10 and 18. At these camps, young people enjoy sporting and cultural activities and work on therapeutic aspects related to carrying out activities of daily living, planning tasks, wheelchair handling, accessibility, training in the community, etc.
Sports&Life Guttmann Club
The Sports&Life activities programme includes activities aimed at young children. Sports&Life makes it possible to do sport and get involved in other social and cultural activities in a different environment to usual and in an inclusive way, contributing to the mood and health of participants. The activities, organised in partnership with other specialised organisations, are coordinated and supervised by the Institut Guttmann and are always accompanied and supervised by hospital staff.